Tentative
Syllabus Math 3066
|
Course: |
Math 3066 4 credits |
GEOMETRY
AND TECHNOLOGY IN THE MIDDLE SCHOOL
MATHEMATICS CLASSROOM Fall 2010 |
|
Department: |
Mathematics
and Computer Science |
|
|
Program(s): |
||
|
Meeting: |
9:00-9:50 AM
MWF |
HS 231 |
|
Extras: |
|
|
|
Dr. Glen
Richgels |
HS 360 Office:
218-755-2824 Email:
grichgels@bemidjistate.edu www:
http://faculty.bemidjistate.edu/grichgels/ |
|
|
7- 8 M-F 11-12 M-F |
|
|
|
3066 GEOMETRY
AND TECHNOLOGY IN THE MIDDLE SCHOOL
MATHEMATICS CLASSROOM (4 credits) This
course helps meet the licensure rule with respect to concepts of patterns,
shape and space; spatial
sense; plane, solid, and coordinate geometry systems; generalizing geometric
principals; limits, derivatives and integrals; and appropriate use of technology
in the classroom. |
||
|
Prerequisite: |
|
|
|
Professional
Education Mission Statement |
Bemidji State
University prepares teachers through inquisitive, involved, reflective
practice. The framework outlining our program sets a standard that is
rigorous, exemplary and innovative. The curricular structure is research
based and organized around the Standards of Effective Practice. Graduates are
proficient, collaborative, technologically literate and environmentally aware
teachers, who work effectively in various settings with diverse learners. |
|
|
Text: |
|
|
|
Recommended: |
Mathematics
for Elementary Teachers a Contempory Approach, |
|
|
Technology: |
|
A calculator
or computer |
Attendance by all students is expected
for all classes.
Homework: Homework assignments will be made in
class. You should come prepared to
discuss the various reading assignments and compare and contrast them with what
you have observed in schools.
Class participation and
quizzes: Class participation is expected and in
order to participate you need to be present.
Exams: Exams will be
approximately tri-weekly. There will be a final exam.
Evaluation:There will
be 3-5 tests given throughout the quarter. Quizzes may be given frequently and may be unannounced. The content for the quizzes and tests
will be based on assignments, classroom discussion and lecture, and textbook
material.
Grades: Grades will be based on the homework, quizzes, tests, and final
exam.
Homework,
Quizzes - one-sixth
Tests -
one-half
Final -
one-third
The
following grading scale will be used to determine grades:
A 90%
- 100%
B 80%
- 89%
C 70%
- 79%
D 60%
- 69%
A grade of C or better indicates that the student has successfully
met the competencies measured in this class through discussion, homework, and
projects.
Incomplete: An incomplete (I) grade will only be
given in documented emergency situations. BSU policies will be followed.
Students are expected to practice
the highest standards of ethics, honesty, and integrity in all of their
academic work. Any form of
academic dishonesty (e.g. plagiarism, cheating, misrepresentation) may result
in disciplinary action. Possible
disciplinary actions include failure for part or all of the course, as well as
suspension from the University.
NOTE: Upon request, this document
and others distributed in this course can be made available in alternate
formats. If you have a documented disability and need accommodations for
this course please contact the instructor, the Disability Services Office in 202 Sanford Hall, Bemidji
State University or Kathi Hagen in the Office for Students with Disabilities at
755-3883 for assistance.. Any other questions about this course should be
directed to the instructor.
Change in
Course Syllabus:
The Instructor reserves the right to change this syllabus as this course
proceeds if the need arises. Should a change be required the class will be
notified.
Course
Outline:
|
(1) concepts of patterns,
relations, and functions: |
|
|
|
(e) apply properties of
boundedness and limits to investigate problems involving sequences and
series; and |
|
|
(f) apply concepts of derivatives
to investigate problems involving rates of change; |
|
(4) concepts of shape and space: |
|
|
|
(a) shapes and the ways in which
shape and space can be derived and described in terms of dimension,
direction, orientation, perspective, and relationships among these
properties; |
|
|
(b) spatial sense and the ways in
which shapes can be visualized, combined, subdivided, and changed to
illustrate concepts, properties, and relationships; |
|
|
(c) spatial reasoning and the use
of geometric models to represent, visualize, and solve problems; |
|
|
(d) motion and the ways in which
rotation, reflection, and translation of shapes can illustrate concepts,
properties, and relationships; |
|
|
(e)
formal and informal argument, including the processes of making
assumptions; formulating, testing, and reformulating conjectures; justifying
arguments based on geometric figures; and evaluating the arguments of others; |
|
|
(f) plane, solid, and coordinate
geometry systems, including relations between coordinate and synthetic
geometry and generalizing geometric principles from a two-dimensional system
to a three-dimensional system; |
|
|
(g) attributes of shapes and
objects that can be measured, including length, area, volume, capacity, size
of angles, weight, and mass; |
|
|
(h) the structure of systems of
measurement, including the development and use of measurement systems and the
relationships among different systems; |
|
|
(i) measuring, estimating, and
using measurements to describe and compare geometric phenomena; |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assignments:
- 2 COMPUTERS - F eatures and Prices
- Computer Terms
- E-mail game (15)
- Software Review (6)
- WWW Review (6)
- Java Applets (6)
- Home Page
- Logo Project
- Grade Book Comparison
- M&M Spreadsheet Project
- Tinker Plots / Fathom Data Project
- Van Hiele Levels
- GSP Geometry Relationships
- GSP Geometry Theorem
- GSP Sliders
- Circles and Angles
- Lego - Robotics
- Trigonometry Measurement
- Cinderella
- Tessellmania
- Geometric Golfer
- Building Perspectives (Both)
- Calculus
- Instructional Lesson and Task (Graduate Students only)
- Final Paper
- Final Evaluation
Instructional Strategies used by
instructor in course:
PolyaŐs problem solving steps
1.
Understand
the problem
- Devise a plan
- Carry out the plan
- Reflect
Lesson
Sequencing
Intuitions
Þ
Concrete ó
Semi-Concrete ó Abstract
GlenŐs
Teaching/Learning Principles
1.
Teach
the way students learn
2.
Use
group work, heterogenous, 3-4, change monthly
3.
Communication
student ó student
4.
Communication
teacher ó student
5.
Multiple
solution paths
6.
Use
contextual settings / problem solving
7.
Assessment
a. Grading
b. To inform instruction
Updated
by Glen Richgels
February 26, 2010
TENTATIVE
Daily Course Outline
|
Assign 1 |
|
|
Assign 2 |
Computer terms (30) |
|
Assign 3 |
Software review (6 programs for 30) |
|
Assign 4 |
WWW Review (6 sites for 30) |
|
Assign 5 |
Java Applets (6 applets for 30) |
|
Assign 6 |
E-mail game (20) |
|
Assign 7 |
Home Page (30) |
|
Assign 8 |
|
|
Assign 9 |
|
|
Assign 10 |
|
|
Assign 11 |
|
|
Assign 12 |
Van Hiele Levels (10) |
|
Assign 13 |
|
|
Assign 14 |
|
|
Assign 15 |
Circles and angles (20) |
|
Assign 16 |
Cinderella (20) |
|
Assign 17 |
Lego robotics (30) |
|
Assign 18 |
|
|
Assign 19 |
Limits (20) |
|
Assign 20 |
Derivatives (20) |
|
Assign 21 |
Integrals (20) |
|
Assign 22 |
Board of Teaching Standards
8710.3320 MIDDLE LEVEL
ENDORSEMENT LICENSE FOR TEACHERS OF MATHEMATICS.
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science
|
EVIDENCE OF LEARNING & ASSESSMENT
OPPORTUNITIES |
||
|
8710.3320
MIDDLE LEVEL ENDORSEMENT LICENSE FOR TEACHERS OF MATHEMATICS |
Course ID Number |
Activity or unit |
Assessment |
|
(1) concepts of patterns,
relations, and functions: |
|
|
|
|
(e) apply properties of
boundedness and limits to investigate problems involving sequences and
series; and |
M3066 |
Cube stacking; fib/lucas seq/ratios; |
|
|
(f) apply concepts of derivatives
to investigate problems involving rates of change; |
M3066 |
Graph tangent lines at a point for polynomial functions |
|
|
(4) concepts of shape and space: |
|
|
|
|
(a) shapes and the ways in which
shape and space can be derived and described in terms of dimension,
direction, orientation, perspective, and relationships among these
properties; |
M3066 |
Locate a point in space with different coordinate systems;
fractal dimension ck www |
|
|
(b) spatial sense and the ways in
which shapes can be visualized, combined, subdivided, and changed to
illustrate concepts, properties, and relationships; |
M3066 |
Area and volume calculations |
|
|
(c) spatial reasoning and the use
of geometric models to represent, visualize, and solve problems; |
M3066 |
Calculate the volume of a sphere (and others) |
|
|
(d) motion and the ways in which
rotation, reflection, and translation of shapes can illustrate concepts,
properties, and relationships; |
M3066 |
Flips, slides, turns, composition of functions |
|
|
(e)
formal and informal argument, including the processes of making
assumptions; formulating, testing, and reformulating conjectures; justifying
arguments based on geometric figures; and evaluating the arguments of others; |
M3066 |
Circles and angles system; sum of angles in a triangle in
geometries; number of regular polygons and polyhedra; taxi-cab geometry |
|
|
(f) plane, solid, and coordinate
geometry systems, including relations between coordinate and synthetic
geometry and generalizing geometric principles from a two-dimensional system
to a three-dimensional system; |
M3066 |
Distance between two points, 1,2,3,n-D |
|
|
(g) attributes of shapes and
objects that can be measured, including length, area, volume, capacity, size
of angles, weight, and mass; |
M3066 |
Comparison of geometric solids; ?? |
|
|
(h) the structure of systems of
measurement, including the development and use of measurement systems and the
relationships among different systems; |
M3066 |
Comparison of English and Metric systems including
evolution and utility |
|
|
(i) measuring, estimating, and
using measurements to describe and compare geometric phenomena; |
M3066 |
Construct tools to measure height and distance (transit);
similarity, law of sines, cosines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
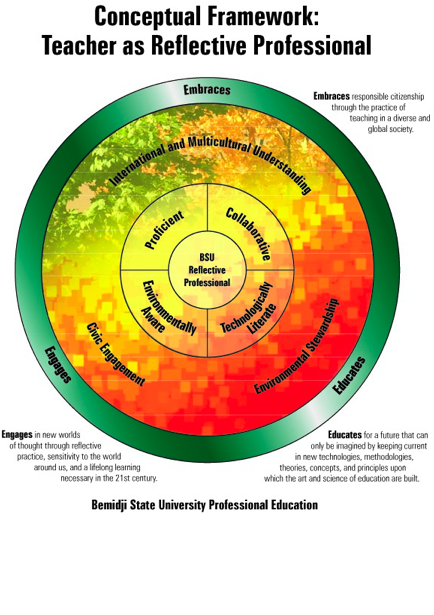
Professional
Education Mission Statement |
Bemidji State
University prepares teachers through inquisitive, involved, reflective
practice. The framework outlining our program sets a standard that is
rigorous, exemplary and innovative. The curricular structure is research
based and organized around the Standards of Effective Practice. Graduates are
proficient, collaborative, technologically literate and environmentally aware
teachers, who work effectively in various settings with diverse learners. |
The middle level teachers from BSU that take the
campus M3066 class[u1] will increase their content knowledge and understanding of how students
learn as they experience studying fundamental operations, probability,
statistics, and foundations of geometry. M3066 is a mixture of challenging
students in the understanding of number sense, discrete mathematics and experiencing activity
based pedagogy. This translates into a more positive attitude toward
mathematics for themselves that hopefully they will take with them into their
teaching.
The best practices of activity oriented learning
is demonstrated in[u2] class from day one. In addition group work and collaborative learning are
encouraged and used almost daily. These best practices are discussed at the
beginning of the course and pointed out and discussed throughout the semester.